How to convert regular & irregular verbs to simple past?
क्रियाओं के SIMPLE PAST (Simple Past of Regular Verbs):

SIMPLE PAST का उपयोग उस क्रिया को वर्णन करने के लिए किया जाता है जो पूर्व में हुई और पूर्ण हो गई थी।
सामान्यत: आम रूप से, क्रियाओं को Simple Past में बदलने के लिए हमें उनके अंत में “-ed” जोड़ना पड़ता है। इसमें कुछ अपवाद हो सकते हैं, जो विशिष्ट स्थितियों के लिए विशेष निर्देश देते हैं।
ध्यान देने योग्य बातें:

सामान्य क्रियाएँ:
- यदि कोई क्रिया सामान्य है और उसका अंत -e से होता है, तो हमें उसके अंत में -d जोड़ना है, जैसे “hate” का “hated” बनता है।
- यदि क्रिया वर्ण -y के साथ समाप्त होती है, तो हमें -y को -i में बदलकर उसके अंत में -ed जोड़ना है, जैसे “cry” का “cried” बनता है।
- यदि क्रिया वर्ण -y से पहले एक स्वर वर्ण के साथ समाप्त होती है, तो हमें उसके अंत में -ed जोड़ना है, जैसे “play” का “played” बनता है।
अनियमित क्रियाएँ:
- कुछ क्रियाएँ नियमित रूप से बदली नहीं जातीं, इसलिए इन्हें याद करना होता है, जैसे “say” का “said” और “buy” का “bought”।
इसके अलावा, इस प्रकार के उदाहरणों के माध्यम से बदलाव को समझना और याद करना उचित है, जो विद्यार्थियों को आसानी से सीखने में मदद कर सकता है।
SIMPLE PAST को क्रिया के बेस रूप में -ed जोड़कर बनाया जाता है।
उदाहरण:
- मैंने कल पुस्तक पढ़ी। (I read a book yesterday.)
- हमने एक नया रेस्तरां में खाना खाया। (We ate at a new restaurant.)
- उसने एक नया गाना गाया। (He sang a new song.)
अनियमितताएँ:
साधारित क्रियाओं के SIMPLE PAST को बनाने के लिए -ed जोड़ा जाता है, लेकिन कुछ क्रियाएं इस नियम से अलग हैं।
o उदाहरण: उसने इसे समझा। (He understood it.)
o उदाहरण: मैंने उसे देखा। (I saw him.)
DO और GO के SIMPLE PAST में अनियमितता है:
- उदाहरण: वह बहुत काम करता था, लेकिन अब वह विराम कर चुका है।
- (He used to work a lot, but now he has retired.)
- SAY और BUY के SIMPLE PAST में अनियमितता है:
- उदाहरण: मैंने कहा कि मैं उससे मिला था, लेकिन वह याद नहीं करती।
- (I said I had met her, but she doesn’t remember.)
FLY के SIMPLE PAST में अनियमितता है:
उदाहरण: हमने हवाई जहाज़ से सफर किया।
- (We flew by plane.)
Negation:
- SIMPLE PAST की negation के लिए “did not” या “didn’t” का उपयोग किया जा सकता है, और क्रिया का बेस रूप बरकरार रहता है।
- उदाहरण: मैंने उससे मिला नहीं। (I didn’t meet her.)
- उदाहरण: हमने वहाँ नहीं जाया। (We didn’t go there.)
- उदाहरण: उसने वह गाना नहीं गाया। (He didn’t sing that song.)
क्रियाएँ और उनका भूतकाल:
- Walk (चलना)
- He walked to the store yesterday.
- He didn’t walk to the store yesterday.
- Push (धक्का देना)
- She pushed the door open.
- She didn’t push the door open.
- Greet (स्वागत करना)
- We greeted our guests warmly.
- We didn’t greet our guests warmly.
- Cover (ढ़ाना)
- The chef covered the pot while cooking.
- The chef didn’t cover the pot while cooking.
- Hate (नफ़रत करना)
- They hated the movie.
- They didn’t hate the movie.
- Seize (पकड़ना)
- The police seized the illegal goods.
- The police didn’t seize the illegal goods.
- Hope (आशा करना)
- She hoped for a better future.
- She didn’t hope for a better future.
- Assume (मान लेना)
- The student assumed the answer was correct.
- The student didn’t assume the answer was correct.
- Tie (बाँधना)
- He tied his shoes before leaving.
- He didn’t tie his shoes before leaving.
- Free (मुक्त करना)
- The activist freed the captured animals.
- The activist didn’t free the captured animals.
इन उदाहरणों में, SIMPLE PAST को बनाने के लिए शाब्दिक रूप में -ed जोड़ा जाता है और उसका असन्तुलन “did not” या “didn’t” के साथ किया है।
विभिन्न अंतों के आधार पर भूतकाल:
- वर्ण -e से समाप्त होने वाली क्रियाएँ:
- Hate (नफ़रत करना)
- They hated the movie.
- They didn’t hate the movie.
- Seize (पकड़ना)
- The police seized the illegal goods.
- The police didn’t seize the illegal goods.
- Hope (आशा करना)
- She hoped for a better future.
- She didn’t hope for a better future.
- Assume (मान लेना)
- The student assumed the answer was correct.
- The student didn’t assume the answer was correct.
- Tie (बाँधना)
- He tied his shoes before leaving.
- He didn’t tie his shoes before leaving.
- Hate (नफ़रत करना)
- वर्ण -y से समाप्त होने वाली क्रियाएँ:
- Play (खेलना)
- They played football yesterday.
- They didn’t play football yesterday.
- Decay (क्षय होना)
- The old house decayed over time.
- The old house didn’t decay over time.
- Survey (सर्वेक्षण करना)
- We surveyed the area before building.
- We didn’t survey the area before building.
- Enjoy (मज़ा करना)
- She enjoyed the concert last night.
- She didn’t enjoy the concert last night.
- Play (खेलना)
- वर्ण -y से समाप्त होने वाली क्रियाएँ :
- Cry (रोना)
- He cried during the sad movie.
- He didn’t cry during the sad movie.
- Dirty (गंदा करना)
- They dirtied their clothes while playing.
- They didn’t dirty their clothes while playing.
- Magnify (बढ़ाना)
- The scientist magnified the image for analysis.
- The scientist didn’t magnify the image for analysis.
- Cry (रोना)
- वर्ण -y से समाप्त होने वाली साधारित क्रिया :
- Fly (उड़ना)
- The bird flew across the sky.
- The bird didn’t fly across the sky.
- Fly (उड़ना)
- वर्ण से समाप्त होने वाली क्रियाएँ:
- Stop (रुकना)
- The car stopped suddenly.
- The car didn’t stop suddenly.
- Prefer (पसंद करना)
- She preferred tea over coffee.
- She didn’t prefer tea over coffee.
- Visit (यात्रा करना)
- They visited the museum last weekend.
- They didn’t visit the museum last weekend.
- Develop (विकसित करना)
- The photographer developed the film in the darkroom.
- The photographer didn’t develop the film in the darkroom.
- Stop (रुकना)
- वर्ण -ie से समाप्त होने वाली क्रियाएँ:
- Die (मरना)
- The old tree died last winter.
- The old tree didn’t die last winter.
- Lie (लेटना)
- The cat lay in the sun for hours.
- The cat didn’t lie in the sun for hours.
- Tie (बाँधना)
- He tied a knot in the rope.
- He didn’t tie a knot in the rope.
- Pie (पाई बनाना)
- She made a delicious apple pie.
- She didn’t make a delicious apple pie.
- Die (मरना)
- वर्ण -e से समाप्त होने वाली साधारित क्रियाएँ:
- Bake (बेक करना)
- She baked cookies for the party.
- She didn’t bake cookies for the party.
- Dance (नृत्य करना)
- They danced all night at the wedding.
- They didn’t dance all night at the wedding.
- Smile (मुस्कान करना)
- He smiled when he heard the joke.
- He didn’t smile when he heard the joke.
- Invite (निमंत्रण भेजना)
- We invited friends to the birthday party.
- We didn’t invite friends to the birthday party.
- Bake (बेक करना)
- वर्ण दोहरा होने वाली साधारित क्रियाएँ:
- Swim (तैरना)
- She swam across the lake.
- She didn’t swim across the lake.
- Run (दौड़ना)
- He ran in the morning to stay fit.
- He didn’t run in the morning to stay fit.
- Hit (मारना)
- The baseball player hit a home run.
- The baseball player didn’t hit a home run.
- Hop (उछलना)
- The bunny hopped around the garden.
- The bunny didn’t hop around the garden.
- Swim (तैरना)
- विशेष स्थितियों में साधारित क्रियाएँ:
- Let (इजाज़त देना)
- They let the kids play in the park.
- They didn’t let the kids play in the park.
- Bet (शर्त लगाना)
- He bet on the winning horse.
- He didn’t bet on the winning horse.
- Hit (गाड़ी या पथ को मिलाना)
- She hit the road early in the morning.
- She didn’t hit the road early in the morning.
- Cut (छांटना)
- He cut the paper with scissors.
- He didn’t cut the paper with scissors.
- Let (इजाज़त देना)
यह उदाहरण दिखाते हैं कि क्रियाएँ भूतकाल में कैसे बनती हैं और उनके negative कैसे बनाया जाता है।
Here is a table illustrating different verb endings, the rule for forming the simple past tense, and examples:
| Ending | Rule | Example |
| -e | Add -d | Bake (Baked), Dance (Danced), Smile (Smiled), Invite (Invited) |
| Vowel + -y | Add -ed | Play (Played), Decay (Decayed), Survey (Surveyed), Enjoy (Enjoyed) |
| Consonant + -y | Change -y to -i and add -ed | Cry (Cried), Dirty (Dirtied), Magnify (Magnified) |
| Vowel + Consonant + Vowel | Double the final consonant and add -ed | Dam (Dammed), Beg (Begged), Plan (Planned), Strip (Stripped) |
Here are more examples with various endings:
| Ending | Rule | Example |
| -e | Add -d | Bake (Baked), Dance (Danced), Smile (Smiled), Invite (Invited) |
| -ee | Add -d | See (Saw), Freeze (Froze), Feel (Felt), Agree (Agreed) |
| -ie | Change -ie to -ied | Lie (Lied), Tie (Tied), Die (Died), Untie (Untied) |
| Vowel + -y | Add -ed | Play (Played), Decay (Decayed), Survey (Surveyed), Enjoy (Enjoyed) |
| Consonant + -y | Change -y to -i and add -ed | Cry (Cried), Dirty (Dirtied), Magnify (Magnified) |
| -ow | Add -ed | Follow (Followed), Mow (Mowed), Show (Showed), Grow (Grew) |
| -yze | Change -yze to -yzed | Analyze (Analyzed), Apologize (Apologized), Realize (Realized) |
| -ly | Add -ed | Apply (Applied), Reply (Replied), Identify (Identified) |
| -w | Add -ed | Follow (Followed), Bow (Bowed), Glow (Glowed), Flow (Flowed) |
| -el | Add -ed | Travel (Traveled), Cancel (Canceled), Revel (Reveled) |
| -en | Add -ed | Open (Opened), Listen (Listened), Widen (Widened), Blacken (Blackened) |
These examples cover various endings and demonstrate how regular verbs are converted to the simple past tense.
Vowel + Consonant + Vowel
For regular verbs ending in a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern, you typically double the final consonant before adding -ed to form the simple past tense. Here are some examples:
| Base Form | Simple Past |
| Hop | Hopped |
| Skip | Skipped |
| Run | Ran |
| Swim | Swam |
| Chat | Chatted |
| Hum | Hums |
| Rob | Robbed |
| Slam | Slammed |
| Stir | Stirred |
| Jog | Jogged |
In each case, the final consonant of the base form is doubled before adding -ed to create the simple past tense.
Consonant + -y, & vowel + -y
For regular verbs ending in a consonant + -y or vowel + -y, you change the -y to -i and add -ed to form the simple past tense.
Here are examples:
Consonant + -y:
| Base Form | Simple Past |
| Cry | Cried |
| Try | Tried |
| Fly | Flied (irregular)* |
Vowel + -y:
| Base Form | Simple Past |
| Play | Played |
| Enjoy | Enjoyed |
| Say | Said (irregular)* |
| Buy | Bought (irregular)* |
*Note: Some verbs in the -y category are irregular and don’t follow the regular pattern of changing -y to -i and adding -ed. Instead, they have unique forms in the past tense.
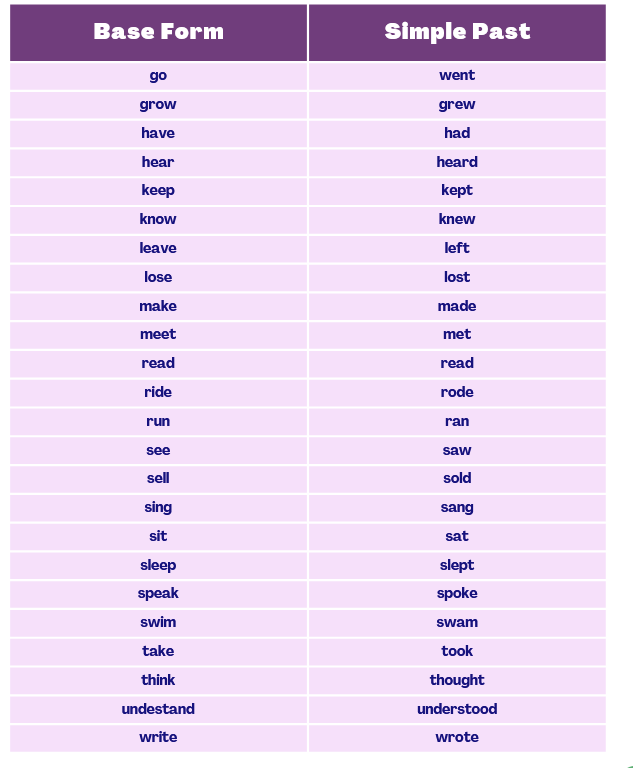
Let’s Revise




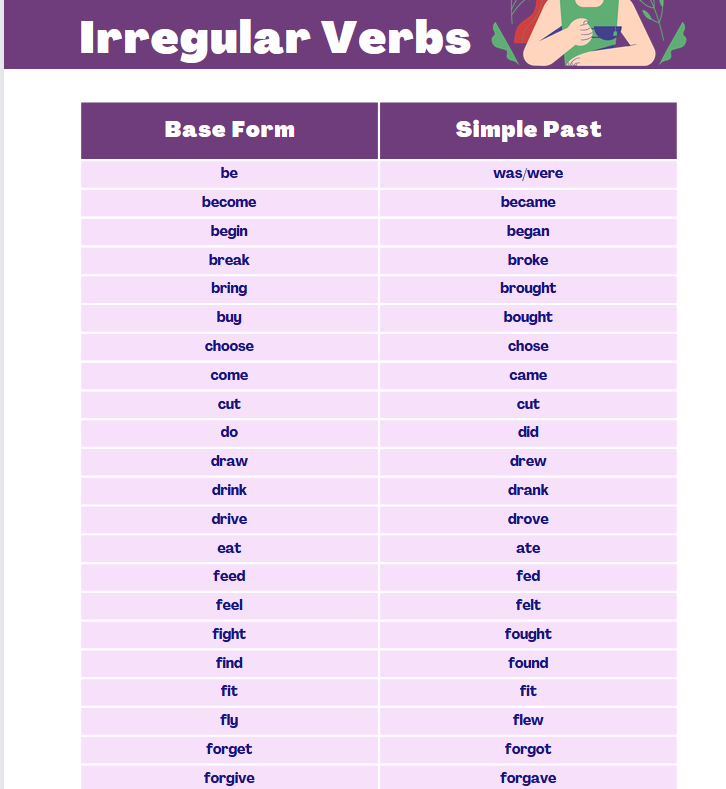
Some More Irregular Verbs & Their Past Forms